The first true bomber-The French Voisin III
The Voisin III was a one of the first of its kind French two-seat bomber and ground attack aircraft of World War I. Its missions included reconnaissance, artillery spotting, training, day and night bombing as well as ground attack. It is also notable for being the first aircraft in the war to win an aerial fight and shoot down an enemy aircraft.
 
Developed by Voisin in 1914 the pusher biplane Voisin III incorporates a light steel frame which made it more durable when operating out of the temporary wartime military aviation airfields. Powered by the 150-horsepower Salmson R9 engine it had a top speed of 113 km/h and range of 200km. The Voisin's Hotchkiss M1914 fuselage mounted machine gun was operated by a standing observer. It could carry a bomb load of approximately 150 kg (330 lb).
The French Air Force purchased large numbers and the Voisin III became the most common Allied bomber during the early years of WWI. Russia bought 800 and produced another 400 under licence. Approximately 100 were built in Italy as well as fifty in the United Kingdom.
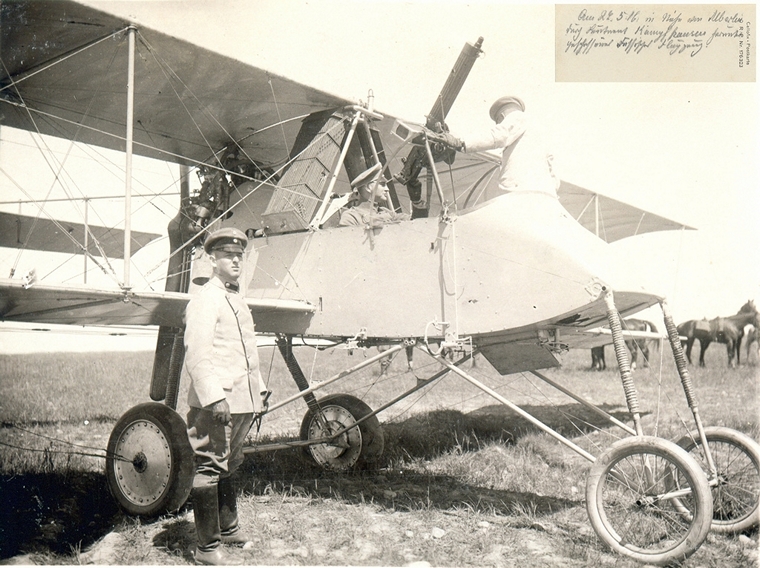

On 5 October 1914 a Voisin scored the first air-to-air kill downing a German Aviatik B.II with machine gun fire. On 14 August 1914 Voisin's attacked German Airship hangars in what is believed to be the first organised bombing attack in aviation history. France was the first country to organize dedicated bomber units on the Western Front, using the Voisin. An almost unopposed bombing campaign was conducted by Voisin's during the early months of 1915.
|
  |